Resistance in Series/Parallel Connection
Resistance in Series:-
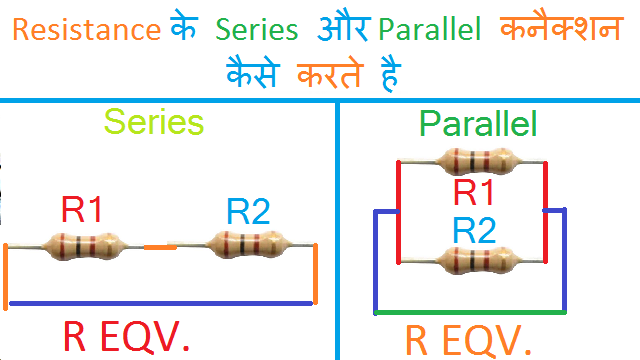
More than one resistances can be connected either in series or in parallel connections. Now if we connect two resistances end on end then they are said to be connected in series. Let’s take an example: Consider three resistances R1 and R2 be connected in series as shown below:

Now Equivalent resistance of this circuit equals to the sum of individual resistances,let’s prove it now:
In series circuit
(1) Same current flows through each resistance.
(2) Voltage drop across each resistance is different.
(3) Net voltage drop applied across circuit equals the sum of all voltage drops across each resistance
Therefore Vs= V1 + V2 = IR1 + IR2
Since Vs= IR
(R is the equivalent resistance of circuit)
Then IR = IR1 + IR2
IR = I (R1+R2)
Cancelling out I from both sides we get
R = R1 + R2
My Youtube Channel
Resistances in Parallel:-
As shown In below figure Resistances are said to be connected in Parallel connection.
In parallel circuit
(1) Potential difference across all resistances is same.
(2) Current flowing through each resistance is different.
(3) Net current flowing through circuit is sum of three currents.
I = t1 + t2 + t3 = V/r1 + V/r2 + V/r3
Also I = V/R
where V is the voltage applied and R is the equivalent resistance of circuit
So V/R = V/r1 + V/r2 + V/r3
1/R = 1/r1 + 1/r2 + 1/r3
Also read: