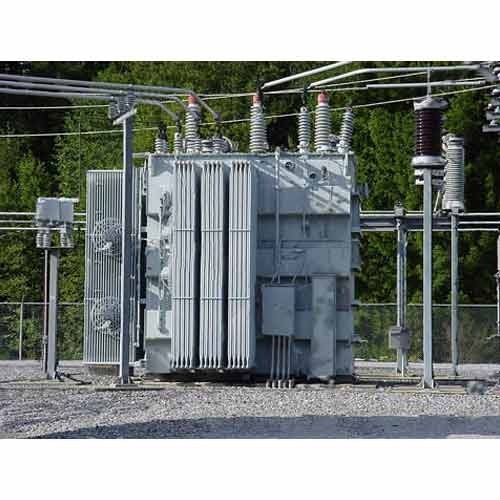
Why we need Transformer?
Since Transformer converts electricity from one voltage level to another voltage level as per our requirement, So Transformer is used for electricity transmission purpose.
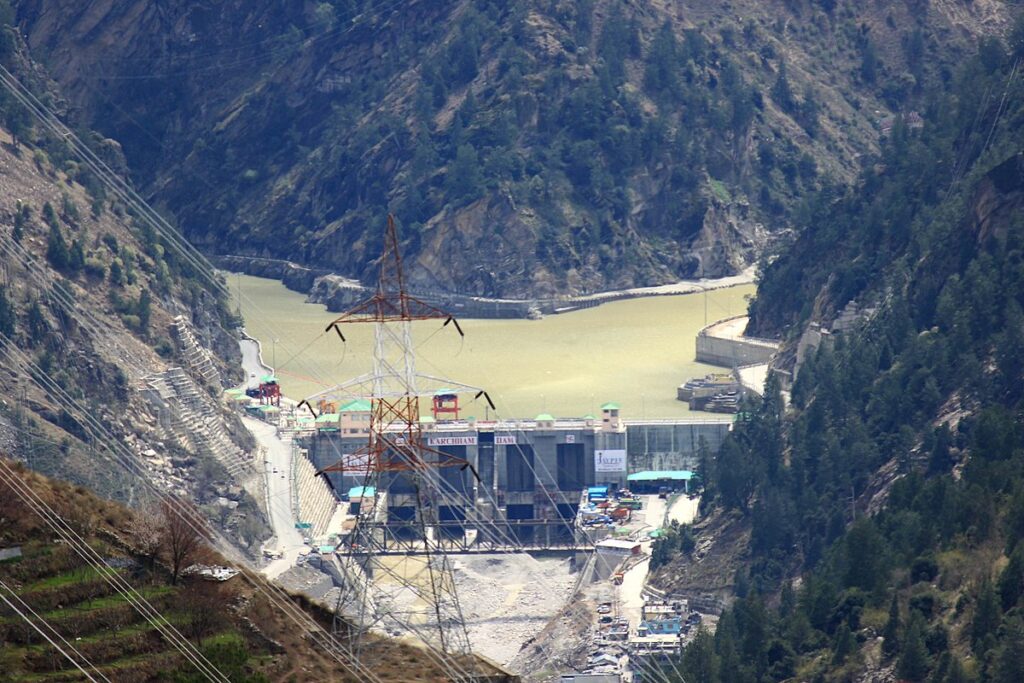

Electricity is generated at Power stations either Hydro Power stations or Thermal Power stations by moving Turbine with water and steam respectively.

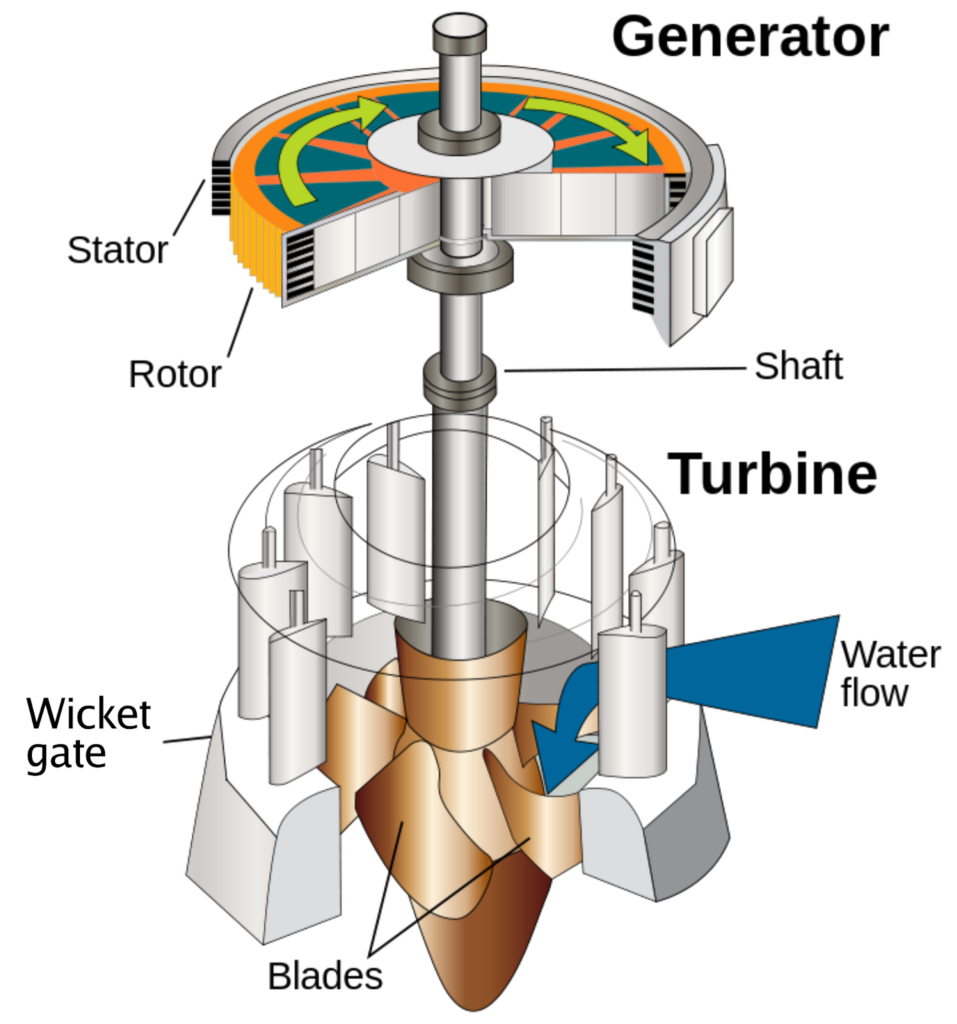
Both types of Power stations are situated very far away around 1000/1200 KM from residential area because Hydro Power stations are situated at hilly areas where dams constructed over river and water stored in the reservoir for turbine running purpose. Since Dams are constructed in-between mountains which are far away from cities, Also Thermal Power stations are situated near the coal mines where coal is easily available and less transportation of coal required so cost reduces since coal mines are available far from cities
Also Read :
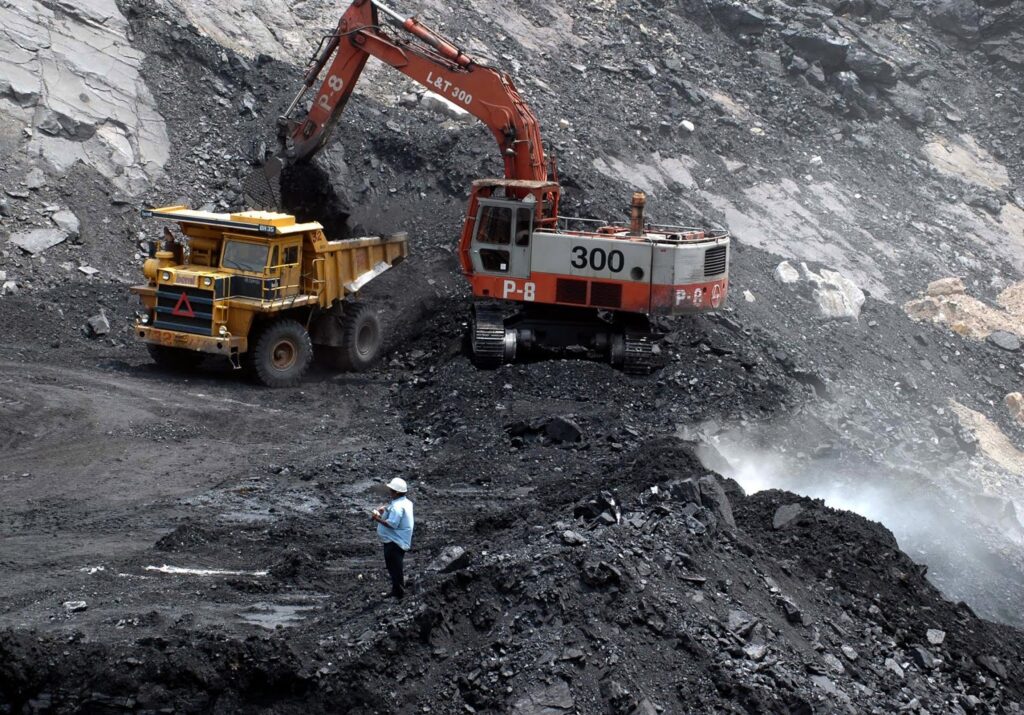

So Thermal Power stations are also situated far away from cities. Now Electricity is generated in Power stations but we have to use this electricity in houses, shops, Industries which is around 1000/1200 KM away from Power stations, So for that we have to transmit electricity through wires. Since Generating Voltage is 11KV

and if we transmit 11KV from Power stations then due to large current heavy transmission losses takes place and very small amount of electricity reaches at consumers end and maximum part get wasted in form of transmission loss by joules law of heating i.e I²R losses. Now only path to transmit electricity is by lower down the current which is only possible by raising the voltage level, since Voltage is inversely proportional to Current i.e. if Voltage is high then current is low and vice-versa. So we have to raise the voltage levels to higher voltages like 132/220/400/765 KV which is only possible with the help of Transformer.

So at Power stations Power Transformer/Step UP Transformer are used which converts low voltage i.e 11 KV into high voltages i.e. 132/220/400/765 KV as per requirement. Then Electricity is transmitted at these voltage levels from Power stations to Sub-stations with the help of large Transmission Towers,which is situated in the vicinity of cities. Due to high voltages transmission losses are almost negligible and maximum electricity reaches at substation.
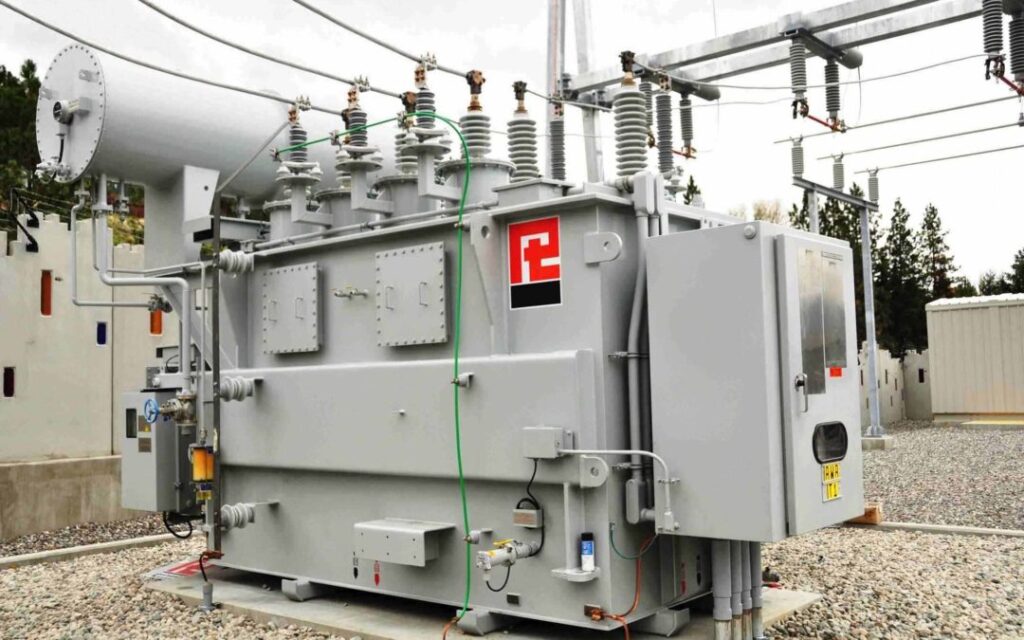

After that at Substation Voltage levels are lower down with the help of again Transformer’s but at sub-stations Step Down Transformers are used where Higher voltages 132/220/400/765 KV gets converted to 33 KV which is also high voltage but used for 30-40 km transmission purpose.
Then this 33 KV Voltage is transmitted to 33 KV Sub-station which is situated in between the city or residential area.Now at 33 KV Sub-station Again Step-Down Transformer is used to convert 33 KV into 11 KV and this voltage is transmitted to Distribution Transformer’s which is installed on H pole structure’s you have already seen near by your houses.

Distribution Transformers are also step down transformers which converts 11 KV into 440 V for three phase and 220 V for single phase which is also called LT supply. Then this voltage is transferred to houses by LT lines and service wires, since Voltage requirement of devices used at our houses is 220 V so LT supply i.e. 220 V is supplied to houses.
So Transformer plays a major role in Electricity transmission and we can’t imagine Electricity transmission without Transformer’s. Also Transformer is very rugged and less maintenance required equipment as there is no moving part in it. It is also called static device.
Also Visit my Youtube Channel for electrical videos

