Transformer MCQ
1. A transformer having 1000 primary turns is connected to a 250-V A.C. supply. For a secondary voltage of 400 V, the number of secondary voltage of 400V, the number of secondary turns should be
- 1600
- 250
- 400
- 1250
Answer: 1
2. A step –up transformer increases
- Voltage
- Current
- Power
- frequency
Answer: 1
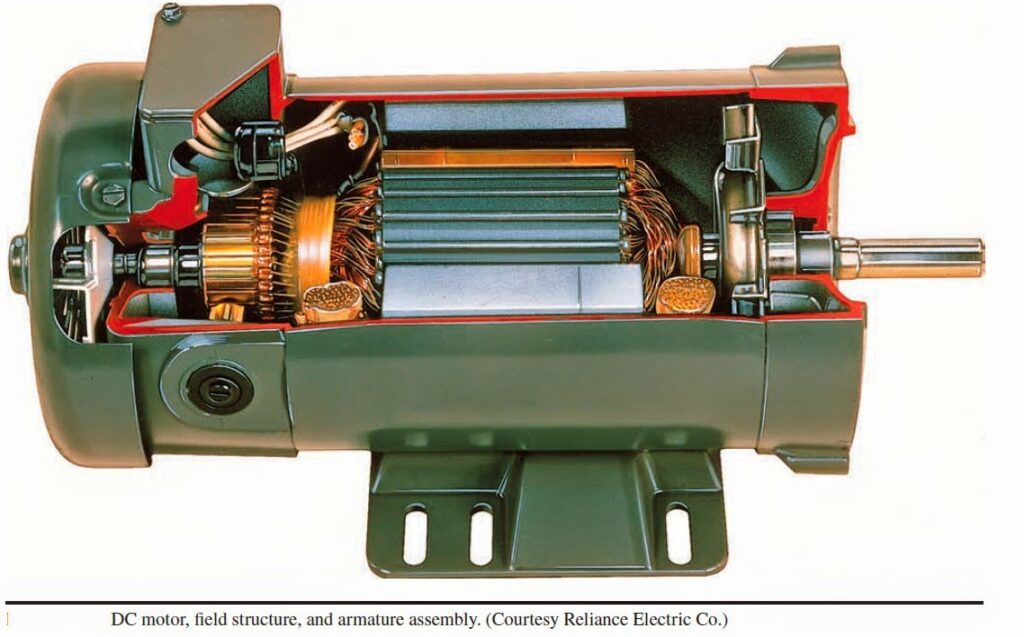
3. The primary and secondary windings of an ordinary2-winding transformer always have
- Different number of turns
- Same size of copper wire
- A common magnetic circuit
- Separate magnetic circuit
Answer: 3
4. In a transformer, the leakage flux of each winding is proportional to the current in that winding becauseer always have
- Ohm’s law applies to magnetic circuits
- Leakage paths do not saturate
- The two windings are electrically isolated
- Mutual flux is confined to the core
Answer: 2
5. In a two-winding transformer, e.m.f. per turn secondary winding is always the induced e.m.f. per turn in primary
- Equal to k times
- Equal to 1/k times
- Equal to
- Greater than
Answer: 3
Related Posts :-
6. In relation to a transformer, the ratio 20:1 indicates that
- There are 20 turns on primary one turn on secondary
- Secondary voltage is 1/20thof primary voltage
- Primary current is 20 times greater than the secondary current
- For every 20 turns on primary, there is one turn on secondary
Answer: 4
7. In performing the short circuit test of a transformer
- High voltage side is usually short circuited
- Low voltage side is usually short circuited
- Any side is short circuited with preference
- None of the above
Answer: 2
8. The equivalent resistance of the primary of a transformer having k=5 and R1=0.1 ohm when referred to secondary becomes __ohm.
- 0.5
- 0.02
- 0.004
- 2.5
Answer: 4
9. A transformer has negative voltage regulation when its load power factor is
- Zero
- Unity
- Leading
- Lagging
Answer: 3
10. The primary reason why open circuit test is performed on the low-voltage winding of the transformer is that it.
- Draw sufficiently large no-load current for convenient
- Requires least voltage to perform the test
- Needs minimum power input
- Involves less core less
Answer: 1
My Youtube Channel