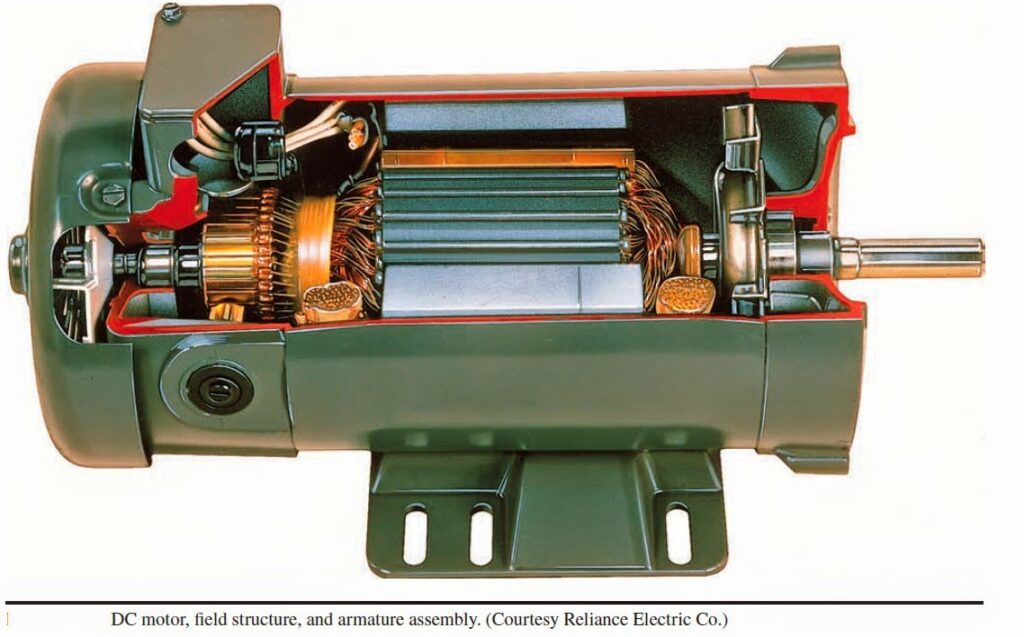
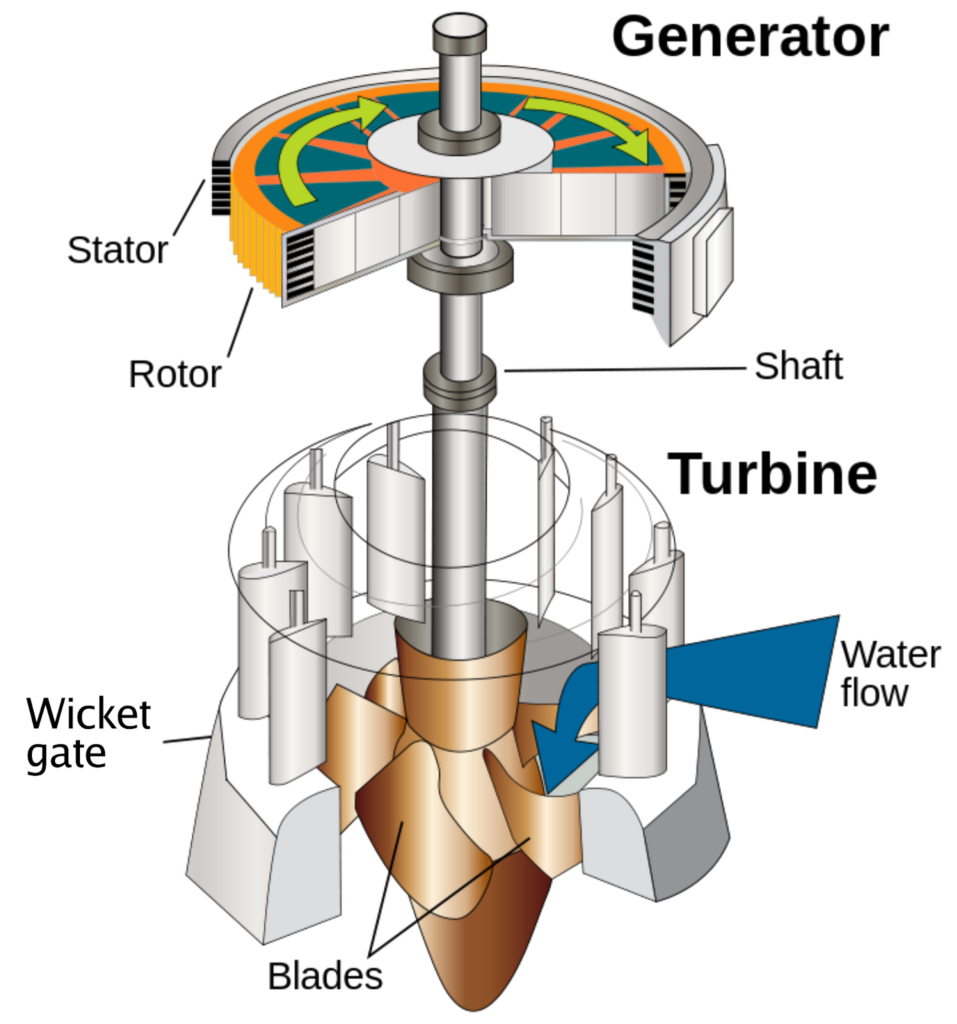
Electrical Machines MCQ
1. The external characteristic of a shunt generator can be obtained directly from its _____________ characterstics.
- internal
- open-circuit
- load saturation
- performance
Answer: 2
2. The slight curvature at the lower end of the O.C.C. of a self-excited dc generator is due to
- V and Ia
- E and Ia
- Eo and If
- V and If
Answer: 3
3. The voltage build up process of a d.c. generator is
- difficult
- delayed
- cumulative
- infinite
Answer: 3
4. For the voltage built up of a self excited d.c. generator, which of the following is not an essential condition?
- there must be some residual flux
- field winding mmf must aid the residual flux
- total field circuit resistance must be less than the critical value
- armature speed must be very high
Answer: 4
Also Read
5. Which of the following d.c. generator cannot build up on open-circuit?
- shunt
- series
- short shunt
- long shunt
Answer: 2
6. If a self excited d.c. generator after being installed, fails to build up on its first trial run, the first thing to do is to
- increase the field resistance
- check armature insulation
- reverse field connections
- increase the speed of prime mover
Answer: 3
7. If residual magnetism of a shunt generator is destroyed accidentally, it may be restored by connecting its shunt field
- to earth
- to an a.c. source
- in reverse
- to a d.c. source
Answer: 4
8. An ideal d.c. generator is one that has _____________ voltage regulation.
- low
- zero
- positive
- negative
Answer: 2
9. The ____________ generator has poorest voltage regulation
- series
- shunt
- compound
- over compound
Answer: 1
10.The voltage regulation of an over compound d.c. generator is always ________
- positive
- negative
- zero
- high
Answer: 2
My Youtube Channel